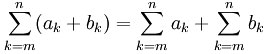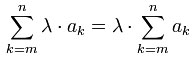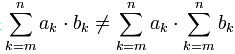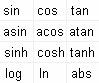
VCmaster is proficient in all mathematical functions of the scientific calculator including all parenthesis levels and exponentiations.
The function descriptions are either entered directly or called up via the menu.
When using the menu VCmaster assists by inserting predefined
functions e.g.
SIN(). The cursor is automatically positioned in the brackets for the function value to be entered,
which can either be a numerical value or a variable.
All functions can be linked, i.e. a function value can also contain a function call (for nesting:
See examples).
The
VCmaster TechEditor can interpret super scripted characters so that the expression X
2 , written with (ALT GR+2 ) is equivalent to the representation X
2 (written with super scripted 2). X
1/3 will also be correctly evaluated,
rendering special exponential functions unnecessary.
Naturally all current mathematical rules apply. If an equation is unsolvable, VCmaster shows a relevant error message. Calculation then continues with the number of decimal places specified. Meaning, if a higher calculation accuracy is required, the number of places after the decimal point has to be increased.
Trigonometric function:
|
|
|
Width b = |
|
|
200. |
00 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
Angle α = |
|
|
45. |
00 ° |
|
|
|
|
|
Height h = |
b * SIN( α ) |
= 141. |
42 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Exponentiation (automatic interpretation of superscripted fields): |
|
|
χ = |
1/(φ+(φ²-λ²)0,5) |
0. |
8083 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Exponentiation (ALT GR+2 * or ALT GR+3 key * ): |
|
|
Width b = |
|
|
10. |
00 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
Height h = |
|
|
20. |
00 mm |
|
|
|
|
|
I = |
b * h3 / 12
|
6666. |
67 mm4 |
|
|
|
|
Note: Depending on the specific charset
Functions such as ABS(), MAX(), MIN(), IF(), AND, OR are realized.
Arguments are separated by semicolons.
The
IF function consists of three elements:
The condition, the formula or the value that is to be used if the condition is fulfilled, and the formula or the value that is relevant if the condition is not fulfilled.

In the IF function all common operators "
="
, "
≠" , "
>" , "
<" , “
≥"
and “≤"" are allowed. Text variables can be compared although only numerical values are
allowed as a result.
The IF function is resolved from right to left. Hence, it makes
sense to utilize brackets in operations.
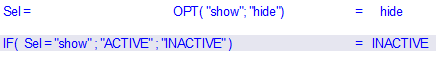
The OPT() function provides predefined options for selection::
Variable X = OPT( "Opt1"; "Opt2"; ... )
Selecting an option is done with a double-click, analogous to the SEL() function. A default of "NULL" defines an empty default (e.g. for result output).
NULL as a variable value: Defines an empty variable. See the
examples as well. A variable of the form Var = "NULL" is suppressed in
result output. Using the expression Var = NULL (without quotation marks)
is permitted.
Note: he OPT() call can be hidden on print. See
Chapter 2.10.3.
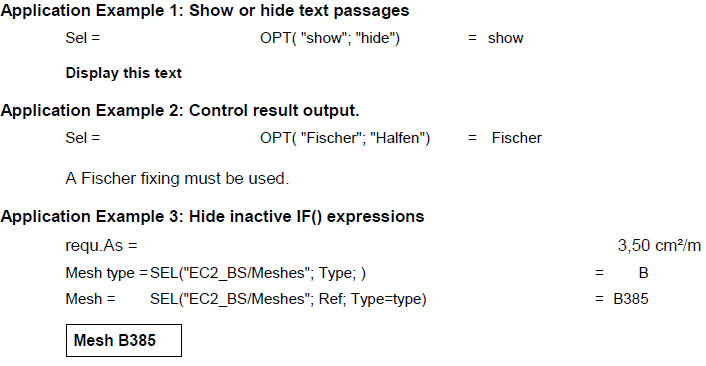
Application Example 1: Show or hide text passagesDisplay
it:

Hidden:
 Application Example 2: Control result output
Application Example 2: Control result output
Input:

Output:
A Fischer fixing must be used.
Application Example 3: Hide inactive IF() expressions
Additional reinforcement required:
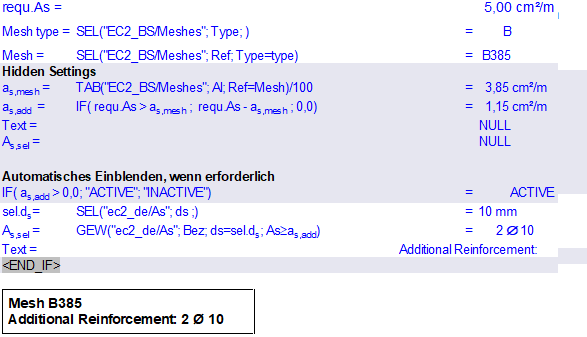
Without additional reinforcement:

The output is fully automatic and adapts depending on requ.As.
Display of the above examples in the output (PDF or print)
The gray-shaded lines are, of course, hidden in the output. It would then look like this:
Both functions are entered in the
graphic formula editor.
The entry of a total corresponds with the mathematical rules.
Note: The index must be identical with the mathematical rules.
Rules:
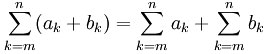
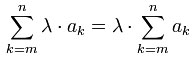
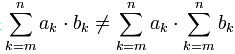 Example
Example:
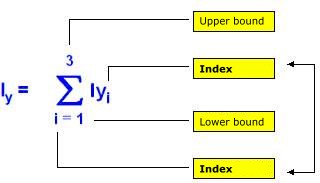
The example shows the following summation:
Iy = Iy1+ Iy2 + Iy3
On generating a formula, every variable can be allocated the unit of
measurement expected by the formula. Alternatively the shortcut
CTRL + #
is available. This function calls for the use of a graphic formula,
which will be generated automatically after text input. The target unit
of measurement is hidden during this operation. It can be modified later
in the Formula Editor.

The fact that formulae are always calculated correctly regardless of
the underlying variable is a major advantage of allocating target units
of measurements.
Using
B= 8,00 dm as shown in the example would
generate the identical value for the area. Using target units of
measurements, errors while copying formulae and templates are avoided. If a
unit of measurement can not be converted, an error message is shown
instead. For validation purposes the converted value can be displayed.
Working with target units of measurements is especially recommended in
countries working with various units and not only with SI-units.
VCmaster is able of working with and converting e.g. British Units.
 VCmaster is proficient in all mathematical functions of the scientific calculator including all parenthesis levels and exponentiations.
The function descriptions are either entered directly or called up via the menu.
VCmaster is proficient in all mathematical functions of the scientific calculator including all parenthesis levels and exponentiations.
The function descriptions are either entered directly or called up via the menu.